Stay Active with COPD: Benefits of Exercise With Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)
CODE
Living with a respiratory condition doesn't have to limit your ability to exercise. Oxygen therapy, when combined with a proper exercise routine, can significantly improve your overall health and well-being. This blog post explores the world of exercise with portable oxygen concentrators (POC), empowering you to stay active and breathe easy.
What is Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)?

Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) involves incorporating physical activity into your treatment plan while using oxygen therapy. This oxygen support helps ensure your body receives enough oxygen during exercise, allowing you to work out safely and effectively. Studies published in the National Institutes of Health [National Institutes of Health (.gov)] database have shown that exercise with portable oxygen concentrators can significantly improve exercise tolerance in patients with COPD, enabling them to exercise for longer durations and at higher intensities compared to those exercising without supplemental oxygen.
Benefits of Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)
There are numerous benefits associated with exercise with portable oxygen concentrators, including:
- Improved exercise tolerance: Oxygen therapy helps reduce shortness of breath and fatigue during exercise, enabling you to exercise for longer durations and at a higher intensity.
- Enhanced cardiovascular health: Regular exercise with portable oxygen concentrators (POC) strengthens your heart and improves circulation.
- Increased muscle strength and endurance: Exercise with portable oxygen concentrators can help build muscle mass and improve stamina, leading to better overall fitness.
- Improved quality of life: By promoting physical activity, exercise with portable oxygen concentrators can boost your energy levels, mood, and overall well-being.
The Role of Portable Oxygen Concentrators in Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)
Portable oxygen concentrators (POC) are lightweight, electronic devices that deliver concentrated oxygen. Unlike bulky stationary concentrators, portable oxygen concentrators are designed for portability, making them ideal for exercise.
Oxygensolve's best-selling NT-02 Portable Oxygen Concentrator exemplifies this perfectly. This 4.85lbs lightweight unit boasts a versatile carrying bag for easy transport. The large, removable battery supports 3-4 hours of continuous use, allowing you to exercise freely without tethering to an outlet.
Here's how a POC like the NT-02 facilitates EWOT:
- Delivers consistent oxygen flow: The NT-02 maintains a stable oxygen concentration of 93±3%, adjustable from 1-5L/min. This ensures your body receives the optimal amount of oxygen throughout your workout.
- Dual delivery modes: The NT-02 features dual oxygen delivery modes that automatically switch to meet your breathing needs, providing a comfortable and efficient experience while doing an exercise.
- Peace of mind features: Built-in alerts and an auto-shutdown timer ensure safe and uninterrupted oxygen therapy during exercise.
Who Can Benefit from Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)?
Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) can be particularly beneficial for individuals with:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): This is the most common condition where exercise with portable oxygen concentrators is used. COPD is a progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe.
- Pulmonary fibrosis: This is a scarring of the lung tissue that can also lead to shortness of breath.
- Emphysema: This is a type of COPD that damages the air sacs in the lungs.
- Other respiratory conditions that limit exercise tolerance: Conditions like cystic fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension may also benefit from exercise with portable oxygen concentrators.
Getting Started with EWOT: Treatment Methods
Before embarking on an exercise with portable oxygen concentrators program, consult your doctor. They will assess your suitability for exercise with oxygen therapy and develop a personalized plan. This plan typically includes:

- Exercise selection: Starting with low-impact activities like walking or stationary cycling is recommended. Gradually increase intensity and duration as your fitness improves. A good starting point is to aim for 20-30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Oxygen flow rate: Your doctor will determine the optimal flow rate to meet your specific needs during exercise. This flow rate is typically measured in liters per minute (L/min).
- Monitoring: Regularly monitoring your oxygen saturation levels with a pulse oximeter is crucial during EWOT sessions. Your doctor will advise you on an acceptable target range for your oxygen saturation during exercise.
Are There Any Risks Associated with Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)?
Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) is generally safe when performed under medical supervision. However, some potential risks exist, including:
- Discomfort: Wearing an oxygen cannula or mask during exercise may cause some initial discomfort. There are different types of cannulas and masks available, so discuss options with your doctor to find one that is most comfortable for you.
- Overexertion: It's essential to listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard during exercise. Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as your fitness improves.
- Safety concerns: Always exercise in a well-ventilated area and have someone nearby in case of emergencies. It's also advisable to inform the person accompanying you about the signs and symptoms of exercise intolerance so they can assist you if needed.
How to Know if Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) is Right for You
Here are some factors you may consider:
- Severity of your respiratory condition: Individuals with more severe respiratory conditions may benefit more from exercise with portable oxygen concentrators than those with milder conditions.
- Current exercise tolerance: If you are already somewhat active, you may be a good candidate for exercise with portable oxygen concentrators .
- Motivation and ability to commit to a program: Exercise with portable oxygen concentrators requires consistent effort to see results.
What are the Exercises While on Oxygen Therapy
Living with a condition that requires oxygen therapy doesn't mean you have to give up on exercise. In fact, incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can significantly improve your overall health and well-being. Here, we explore some exercises specifically recommended for oxygen therapy patients, helping you stay active and manage your symptoms effectively.
Building Leg Strength:
Strong legs are crucial for everyday activities. Here are two simple exercises to target your legs without excessive movement:
-
Calf Raises:
- Stand with your back against a chair for support or place your hands on a wall for balance.
- Inhale and slowly lift your heels off the ground, rising onto your toes.
- Hold this position for a few seconds while exhaling.
- Lower your heels back down to the ground as you inhale slowly.
- Repeat this exercise several times.
-
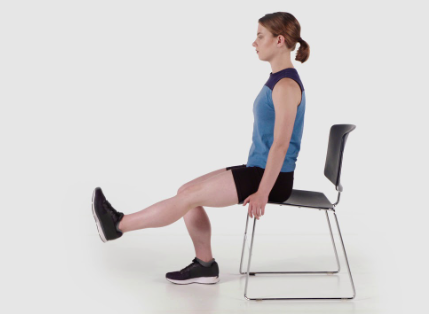
Leg Extensions:
- Sit in a chair with good back support.
- Breathe in and exhale as you extend one leg at a time, straightening it forward without locking your knee.
- Hold for a second, then slowly lower the leg back down as you inhale.
- Repeat this exercise several times with each leg.
Enhancing Arm Strength:
Maintaining upper body strength is equally important. Here are two exercises to target your arms while receiving oxygen therapy:

-
Bicep Curls:
- Using light weights in each hand, breathe in and curl the weights towards your chest.
- Exhale slowly as you lift the weights.
- Lower your arms back down to a 90-degree angle while inhaling again.
- Repeat this exercise several times.
-
Tricep Extensions:
- Lie flat on your back with light weights in each hand.
- Lift and extend your arms so the weights are directly above your chest.
- Slowly lower the weights towards your shoulders, bending your elbows but keeping them close to your body. Pause briefly at the bottom.
- Ensure your elbows remain stationary for maximum benefit.
- Inhale as you return to the starting position and repeat several times.
Boosting Endurance with Low-Impact Cardio:
Low-impact cardio exercises are excellent for building endurance without putting excessive strain on your lungs. Here are some examples:

- Indoor Cycling: Stationary cycling allows for controlled exercise without the stress of uneven terrain.
- Walking: Walking is a fantastic choice for most people. Start with short walks and gradually increase the duration and intensity as your fitness improves.
- Tai Chi: This gentle form of exercise combines slow, controlled movements with deep breathing, promoting balance, flexibility, and overall well-being.
Remember:
- Start Low, Go Slow: Begin with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the difficulty as you get stronger.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay close attention to your breathing and energy levels during exercise. Don't hesitate to take breaks and stop if you experience any discomfort.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: It's always advisable to consult your doctor or a physical therapist before starting any new exercise program. They can create a personalized plan considering your specific needs and limitations.
By incorporating these exercises into your routine, along with your oxygen therapy, you can manage your symptoms effectively, improve your overall health, and experience a more active lifestyle.
Enhancing Your EWOT Experience: Helpful Tips
Here are some tips to optimize your EWOT experience:
- Warm-up and cool-down: Always include a proper warm-up before exercise and a cool-down afterward to prevent injury. A good warm-up should gradually increase your heart rate and blood flow, while a cool-down helps your body return to its resting state.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after your workout. Dehydration can worsen respiratory symptoms and make exercise more difficult.
- Comfortable clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing for optimal comfort during exercise. Avoid wearing tight clothing that could restrict your breathing.
- Listen to your body: Don't hesitate to take breaks when needed and stop if you experience any discomfort. Signs of exercise intolerance during EWOT may include increased shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or lightheadedness.
- Work with a qualified therapist: Consider working with a physical therapist or respiratory therapist who can help you develop a safe and effective exercise program tailored to your needs.
Conclusion: Breathe Easy, Live Actively with Oxygensolve
By incorporating exercise with portable oxygen concentrators into your routine, you can reap the benefits of improved exercise tolerance, enhanced cardiovascular health, increased muscle strength and endurance, and an overall better quality of life. If you have a respiratory condition that limits your ability to exercise, talk to your doctor about whether EWOT might be a right fit for you.
Oxygensolve's NT-02 Portable Oxygen Concentrator is an excellent choice for those seeking a lightweight, portable, and reliable option for oxygen therapy during exercise. With its long battery life and adjustable oxygen flow rate, the NT-02 can help you stay active and breathe easy wherever you go. Visit our website today to learn more about the NT-02 and other oxygen therapy solutions from Oxygensolve.




















